Abdominal Surgery
This is the branch that deals with the treatment of diseases of the abdominal cavity and, in particular, the treatment of abdominal wall defects such as hernias and the treatment of pathologies of abdominal organs such as stomach, liver, pancreas, small intestines and large intestines.
Abdominal surgery is distinguished between Laparotomic and Laparoscopic surgery according to the type of approach chosen.
Laparotomic (Open) surgery involves a classic approach with an incision of the anterior abdominal wall to gain access to the abdominal cavity.
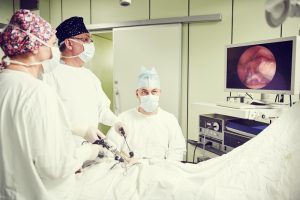
Laparoscopic surgery or Video Surgery (VLC) involves the introduction of a Trocar through small holes in the abdomen, the subsequent insertion of an optic cable through said Trocar, with images being transmitted on a screen, and the insertion of surgical accessories.
VLC has the advantage of being less invasive than Open surgery, reducing postoperative pain and patient recovery time.
Sometimes, however, operating times may be longer and costs may be higher than with open surgery.
In abdominal surgery, the following diseases can be addressed with both laparotomic and laparoscopic approaches:
- Diseases related to the gallbladder and the biliary tract
- Pancreatic diseases
- Diseases of the adrenal glands
- Digestive tract diseases
- Spleen Diseases
- Abdominal wall defects
- Urinary tract diseases
- Reproductive tract diseases
- Serious obesity-related diseases (Bariatric Surgery)
- Pelvic floor anatomical-functional alterations
- Hemorrhoids
- Urinary incontinence
- Colposacroplexis